Pressure Measurement Fundementals
Pressure Definition and Units
Pressure Definition and Units is fundamentally the amount of force applied over a specific area. Think of it like standing on snow - with regular shoes you sink because your weight (force) is concentrated on a small area, but with snowshoes you stay on top because the same force is spread over a larger area.
Pressure is defiened as:
where :
- F = Force (in Newtons, N)
- P = Pressure (in Newtons per square meter, N/m²)
- A = Area (in square meters, m²)
This equation can be rearranged to: P = F/A, showing that pressure decreases
when the same force is applied over a larger area.
Units for measuring pressure:
- PSI (Pounds per Square Inch): Common in US industries
- Pascal (Pa): The SI unit, where 1 Pa = 1 Newton per square meter
- Bar: Popular in Europe, where 1 bar ≈ 14.5 PSI
- Inches of Water Column (inH2O): Often used for low pressures in HVAC systems
- Torr or mmHg: Used in vacuum applications
See my pressure conversion calculator here
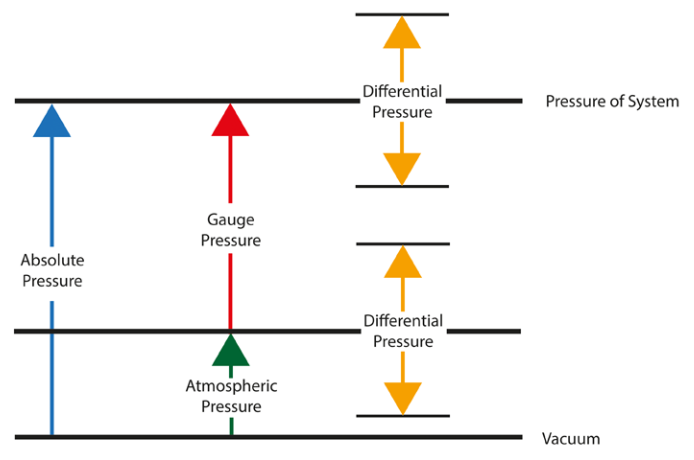
Types of Pressure Measurements:
- Absolute Pressure: Measured relative to perfect vacuum
- Gauge Pressure: Measured relative to atmospheric pressure
- Differential Pressure: The difference between two pressure points
- Vacuum: Pressure lower than atmospheric pressure
Types of Pressure Measurements
When working with pressure in industrial processes and everyday applications, it's crucial
to understand that pressure can be measured in different ways depending on the reference
point used. Just like measuring height can be relative to sea level or ground level,
pressure measurements also need a clear reference point to be meaningful.
Let's explore the four main types of pressure measurements:
- Absolute Pressure: Measured relative to perfect vacuum - Imagine a completely empty container with no air molecules at all. This is our zero point for absolute pressure measurements. Every pressure reading is measured upward from this perfect vacuum. Space, for example, has an absolute pressure very close to zero.
- Gauge Pressure: Measured relative to atmospheric pressure - This is what most everyday pressure gauges display. When you check your tire pressure, you're reading gauge pressure. The gauge automatically subtracts atmospheric pressure from its reading, showing you only the pressure above the normal air pressure around us.
- Differential Pressure: The difference between two pressure points - This measures the pressure difference between any two points, regardless of their absolute pressures. It's particularly important in filtration systems where we need to know the pressure drop across a filter, or in ventilation systems where we measure the pressure difference between inside and outside a building.
- Vacuum: Pressure lower than atmospheric pressure - While technically a negative gauge pressure, vacuum measurements are often given special attention because they behave differently than positive pressures. In vacuum systems, we're measuring how much lower the pressure is compared to the atmosphere around us.
The pressure variables use the letter P with descriptive subscripts:
- Absolute pressure: Pabs
- Atmospheric pressure: Patm, sometimes written as Pamb as in ambient pressure
- Gauge pressure: Pg
- Differential pressure: ΔP or DP
Formulas for the differential pressures
Other Pressure References
- Overpressure: Overpressure can mean two things in this context. First, overpressure in relation to atmospheric pressure means the pressure is higher than atmospheric pressure. Second, overpressure occurs when a pressure-measuring instrument is subjected to pressure higher than its specified maximum operating pressure.
- Underpressure: Underpressure can mean two things in this context. First, underpressure in relation to atmospheric pressure means the pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure (also known as vacuum or negative gauge pressure). Second, underpressure occurs when a pressure-measuring instrument is subjected to pressure lower than its specified minimum operating pressure.
- Static pressure: Static pressure is the pressure exerted by a fluid (liquid or gas)
that is at rest or moving, measured perpendicular to the flow direction. It represents the actual
pressure that acts on the walls of a container or pipe.
Key characteristics of static pressure:- It acts equally in all directions within a fluid at a given point
- It's measured using pressure taps or ports positioned flush with the pipe/vessel wall
- It represents the "true" pressure within a system
- It's what most standard pressure gauges and transmitters measure
- Dynamic pressure: Dynamic pressure is the pressure component that results
from the kinetic energy of a moving fluid. It represents the pressure difference that
arises due to the fluid's motion.
Key characteristics of dynamic pressure:- It only exists in moving fluids and increases with flow velocity
- It can be calculated using the formula: Pdynamic = ½Ïv² (where Ï is fluid density and v is velocity)
- It's directional (it acts in the direction of fluid flow)
- It cannot be measured directly with standard pressure instruments