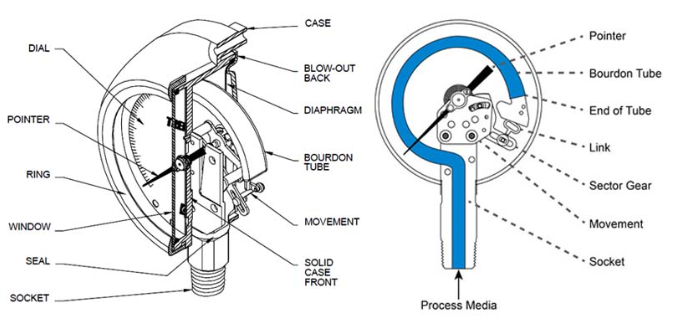
Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge
Bourdon Tube pressure gauge
A Bourdon Tube pressure gauge is a mechanical device that measures
pressure using a curved or coiled metal tube called a Bourdon tube.
Here's how it works:
-
Structure:
The main component is a flattened, curved metal tube (Bourdon tube) that's sealed at one end (End of tube in the image under) and open at the other. The tube has an oval cross-section and is typically made of brass, bronze, or steel. -
Operating Principle:
When pressure enters the open end of the tube, it causes the flattened tube to try to straighten out. This is because the pressure acts more strongly on the larger inner surface area than the smaller outer surface area. The higher the pressure, the more the tube tries to straighten. -
Mechanical Linkage:
The sealed end of the tube is connected to a mechanical linkage system consisting of:- A sector gear that rotates as the tube moves
- A small pinion gear (Shown as "link" in the image under) that meshes with the sector gear
- A pointer (needle) attached to the pinion gear
-
Display:
As pressure increases and the tube straightens, the movement is amplified through the gear system, causing the pointer to move across a calibrated dial. The dial is marked with pressure units (like PSI, bar, or kPa). -
Calibration:
The gauge is calibrated by comparing its readings against known pressure values, and the dial is marked accordingly. The relationship between tube movement and pressure is nearly linear, making these gauges quite accurate within their designed range.
These gauges are widely used in industrial applications because they're reliable, don't require power to operate, and can be made to work with various pressure ranges and fluids.